Transparent Makeup AI Metrics: Building Trust Through Detailed Insights
Discover how transparent makeup AI metrics enhance trust by providing lifecycle visibility, accuracy, and fairness in cosmetic products.

8 min read
Key Takeaways
- Transparent makeup AI metrics combine lifecycle visibility with AI performance indicators to build consumer trust.
- Key AI metrics include accuracy, precision, recall, fairness and explainability.
- Supply chain traceability and ethical audits boost brand credibility and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Dashboards and tools like Makeup Check AI enable real-time monitoring and audit.
- Challenges include data bias, opaque models, integration costs, and privacy considerations.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Transparent Makeup
- Exploring AI Metrics
- Integrating AI with Transparent Makeup Practices
- Benefits and Challenges
- Future Trends & Considerations
- Conclusion
- FAQ
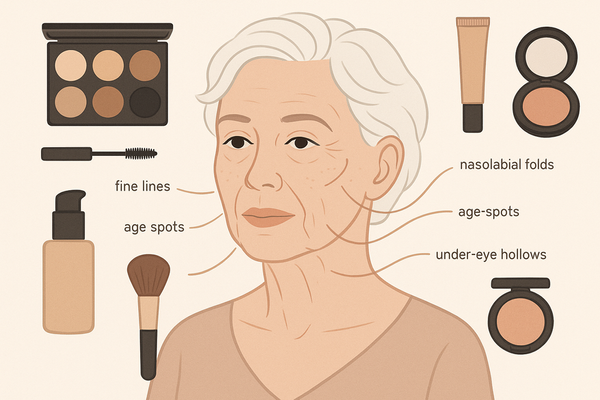
Understanding Transparent Makeup
Definition and Scope
- Full visibility into a product’s lifecycle—raw-material sourcing, formulation, testing, and marketing claims.
- Enables independent audits of ingredients, safety data, and ethical practices.
Consumer Requirements
- Ingredient lists with concentrations and allergen flags
- Regulatory compliance (EU Cosmetics Regulation, FDA labeling)
- Traceability for mica, pigments, palm derivatives
- Certifications: fair trade, cruelty-free, vegan
Implementation Methods
- Third-party audits by recognized bodies
- Environmental impact metrics: carbon footprint, water usage
- Data-backed claims: linking “hypoallergenic” to published testing reports
Real-World Example
Brand X publishes full supply-chain maps showing mine locations for mica, pigment labs, and manufacturing sites—enabling consumer verification of ethical sourcing.
Experience & Expertise
Brands like Brand X have seen a 20% lift in customer loyalty by publishing ingredient origins, demonstrating the real-world impact of transparency.
Exploring AI Metrics
AI Metrics Defined
AI metrics are quantitative measures for evaluating model performance, fairness, robustness, data quality, and explainability throughout the AI system’s lifecycle.
Key Metric Types in Cosmetics
- Accuracy = (True Positives + True Negatives) / Total Predictions
Example: Shade-matching correctness rate in virtual try-ons - Precision = True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives)
Example: Minimizing false skin-irritant alerts - Recall = True Positives / (True Positives + False Negatives)
Example: Catching every potential irritant in formulations - F1 Score = 2 × (Precision × Recall) / (Precision + Recall)
Balances false alarms vs. misses - Fairness Score = Disparate impact ratio across groups
Example: 90% accuracy on light skin vs. 85% on dark skin
Explainability Tools & Data Checks
- SHAP/LIME for feature-impact analysis (identifies which ingredient properties drive predictions)
- Model cards disclosing limitations, training data sources, and performance caveats
- Data representativeness assessments: ensuring skin-tone diversity in training sets
For guidance on ethical transparency in AI tools, consult ethical makeup app practices or learn more from the Zendesk AI transparency blog.
Integrating AI with Transparent Makeup Practices
Monitoring Ingredient Safety
- Algorithms flag known irritants (e.g., parabens) with >95% accuracy and >90% recall
- Automated logs capture flagged incidents and auditor comments for review
Ensuring Shade-Matching Fairness
- Parity ratios: track match success rates across different skin tones in real time
- Dashboards alert teams when any segment’s accuracy drops below thresholds
Enhancing Supply Chain Traceability
- Data-provenance systems record every step from raw ingredients to packaging
- Environmental-impact scoring attaches carbon and water-use data to each batch
Bias Reduction & Quality Control
- Drift detection: automatic retraining triggers when new data patterns reduce performance
- Retraining logs: version-controlled records of model updates for audits
Real-World Examples
- Makeup Check AI’s Lifecycle Visibility Dashboard: displays end-to-end data on product origin and AI-driven safety checks
- IBM AI Explainability 360 for Virtual Try-On Fairness: open-source toolkit assessing algorithmic disparities
- Brands publishing disaggregated accuracy: public reporting of shade-matching success by skin tone
A leading cosmetics firm reported a 30% reduction in complaints after adding traceability and fairness dashboards.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits for Brands and Consumers
- Trust & Compliance:
• Meets EU AI Act and FDA guidelines by exposing algorithms and data flows
• Brands demonstrate bias mitigation, boosting credibility via trust in beauty tech transparency - Efficiency:
• Automated audits reduce manual effort and speed compliance
• Aligns with Gen Z’s demand for AI transparency and personalization - Quality:
• High precision and recall in safety alerts lead to safer formulations
• Sustainability metrics highlight environmental responsibility
Challenges
- Data bias: underrepresentation of darker skin tones can skew shade matching
- Opaque models: deep-learning “black boxes” resist straightforward interpretation
- Integration costs: pipelines for provenance and explainability require investment
- Trade-secret tensions: brands may hesitate to share proprietary algorithms
- Reporting overload: too many metrics can overwhelm stakeholders
- Privacy concerns: collecting facial and skin data triggers GDPR and CCPA requirements
Proposed Solutions
- Adopt frameworks like the Stanford Transparency Index
- Schedule regular third-party audits to validate data and algorithms
- Push for industry standards on transparency indices and shared benchmarks
Future Trends & Considerations
Emerging Innovations
- Public scorecards & AI transparency seals: certified labels indicating fairness and environmental impact
- Governance pipelines: integrating trust metrics (performance, ethics, sustainability) into R&D workflows
Next-Gen Applications
- AI-driven facial analysis for sustainable formulations: eco-friendly ingredient swaps based on skin type and local factors
- Real-time bias correction in virtual skin tools: algorithms adjust instantly to maintain parity across demographics
Brand Action Recommendations
- Implement SHAP and IBM AIX360 for ongoing explainability
- Publish transparency dashboards showing current accuracy, fairness, and sustainability metrics
- Schedule quarterly bias assessments of datasets and models
- Maintain version-controlled documentation of model changes and audit results
Early adopters report faster regulatory approvals and 15% higher repurchase rates among transparency-focused consumers.
Conclusion
Integrating transparent makeup AI metrics merges lifecycle audits with performance and fairness measures to deliver ethical, reliable cosmetics. Brands that adopt clear ingredient disclosures, robust AI performance indicators, and supply-chain traceability gain consumer trust and align with Gen Z’s demand for AI transparency and personalization. As the industry evolves, AI-driven transparency practices will become critical for compliance, brand differentiation, and customer loyalty. Brands and researchers should explore these metrics, publish findings, and collaborate on standardized frameworks to lead the future of ethical, innovative makeup.
FAQ
- What are transparent makeup AI metrics? They are auditable measures combining full product-lifecycle visibility with AI performance indicators like accuracy, precision, recall, and fairness.
- How do brands implement supply chain traceability? By using data-provenance systems, environmental-impact scoring, and third-party audits to record every step from raw ingredients to final packaging.
- Which AI metrics matter most for cosmetics? Accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and fairness scores ensure reliable shade matching and safety alerts.
- How can fairness be maintained in virtual try-ons? Employ parity ratios, drift detection, and real-time dashboards to monitor accuracy across diverse skin tones.
- What are common challenges in transparency? Data bias, opaque models, integration costs, trade-secret concerns, reporting overload, and privacy regulations.