Inclusive Beauty Tech: Redefining Accessibility and Personalization in Makeup
Explore how inclusive beauty tech uses AI and AR innovations to enhance accessibility and personalization for all skin tones, genders, and abilities.

6 min read
Key Takeaways
- Inclusive beauty tech uses AI and AR to personalize makeup for all skin tones, genders, and abilities.
- Innovations include AI shade matching, AR try-ons, personalized recommendation engines, and adaptive packaging.
- Challenges remain in shade ranges, marketing norms, packaging accessibility, and digital inclusion.
- Future trends point to wearable monitoring, genomic personalization, and adaptive smart tools.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Inclusive Beauty and Tech Challenges
- Inclusive Beauty Tech Innovations in Makeup
- Inclusive Beauty Tech Packaging and Accessibility
- The Impact and Future of Inclusive Beauty Tech
- Conclusion
Section 1: Understanding Inclusive Beauty and Tech Challenges
inclusive beauty tech challenges
- All genders, including non-binary and gender-fluid consumers
- Every age group, from teens to seniors
- Diverse skin types and textures (oily, dry, combination, acne-prone)
- Individuals with physical disabilities affecting dexterity or vision
Why truly inclusive beauty matters:
- Overcoming historical exclusion that left many skin tones unserved
- Providing products that fit unique skin concerns, textures, and cultural preferences
- Empowering confidence and self-expression through personalized solutions
Current inclusive beauty tech challenges:
• Limited shade ranges in conventional cosmetics often force customers to mix products or shop in multiple brands.
• Gendered marketing campaigns overlook non-binary identities, reinforcing binary norms.
• Inaccessible packaging—small caps, smooth edges, and unreadable fonts—hinder users with limited dexterity or low vision.
• Digital exclusion in beauty apps excludes users with disabilities when interfaces lack screen-reader compatibility or haptic feedback.
Real-world observation: During a virtual focus group, users with arthritis struggled to open sample vials, highlighting the need for universal design. Inclusive UX design and assistive tech features—like voice commands and high-contrast modes—ensure equal access to digital try-on tools and tutorials.
Section 2: Inclusive Beauty Tech Innovations in Makeup
inclusive beauty tech innovations
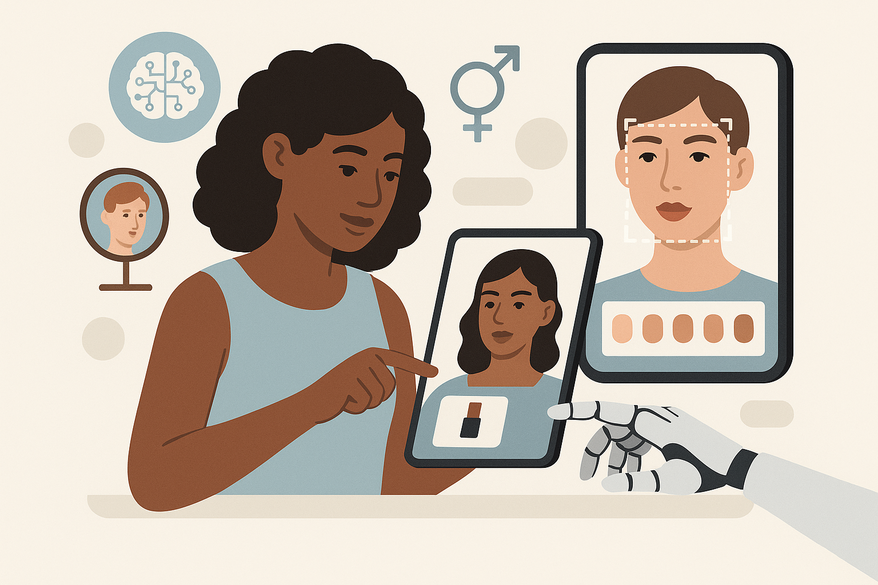
- AI-Powered Foundation Shade Matching
How it works: Deep learning algorithms analyze facial images to identify undertones and recommend precise foundation matches (see skin-tone analyzer).
Benefits: Cuts down on wasted trial samples, reduces return rates, and offers instant, data-backed shade suggestions.
Example: NARS AI Shade Finder uses neural networks to recommend the best match from 40+ shades, improving first-time accuracy by 30% (learn more at foundation shade match guide). - Augmented Reality (AR) Try-On Apps
Definition: AR overlays virtual makeup in real time, letting users experiment with lip colors, eyeshadows, and blush on live video.
Advantages: Mobile and web apps democratize access to professional-level virtual try-ons; global users can test new looks without physical visits.
Limitations: Device camera quality and lighting can affect realism; developers use machine-vision enhancements to improve detection across skin tones.
Explore use cases at virtual makeup try-on use cases. - Personalized Product Recommendation Engines
How algorithms work: They combine user skin data (pH, oiliness, elasticity) with self-reported concerns (acne, pigmentation) to craft custom routines.
Impact: Users receive step-by-step regimens, from cleansers to serums, reducing decision fatigue and boosting regimen adherence. - Integration in R&D and Customer Experience
Virtual Focus Groups: Brands use online communities to test formulas on diverse skin types before mass production.
Real-Time Feedback Loops: AI chatbots and surveys capture satisfaction metrics post-launch, guiding iterative formula tweaks.
Scalable Inclusivity: Cloud-based platforms manage big data from global consumers to identify gaps in shade lines or packaging formats.
Tools like Makeup Check AI demonstrate how inclusive beauty tech can simplify shade matching and virtual try-ons with intuitive interfaces that work across diverse skin tones and lighting. The following video shows how it works:
Section 3: Inclusive Beauty Tech Packaging and Accessibility
inclusive beauty tech packaging accessibility
Adaptive Design in Packaging and Tools
- Ergonomic Containers: Easy-twist caps, pump dispensers, and one-hand operable tubes for users with limited dexterity.
- High-Contrast Labels: Bold, sans-serif fonts against contrasting backgrounds for low-vision consumers.
- Large-Print Instructions: Clear, step-by-step usage guides printed in at least 16-point type.
Smart Packaging Enhancements
- Braille and Tactile Markings: Raised dots on jar lids or tubes identify product type for blind users.
- QR Codes to Audio Descriptions: Scanning codes plays narrated instructions or ingredient info in multiple languages.
- 3D-Printed Custom Applicators: Brands offer on-demand printing of brushes shaped for individual grip preferences.
Case Studies of Inclusive Packaging and Tools
• Baralan’s refillable glass jars with silicone sleeves that double as grips, featuring tactile bands for product differentiation.
• Indie Brand Spotlight: Lip-balm tubes with embossed color names and ergonomic hexagonal shapes to improve hold for trembling hands.
Section 4: The Impact and Future of Inclusive Beauty Tech
future of inclusive beauty tech
Broader Market Opportunities:
Underserved demographics—dark skin neutralizers, gender-neutral palettes, adaptive tools—unlock loyal segments and drive 25% higher repurchase rates for brands with diverse shade lines.
Benefits for Consumers:
Personalized matches and accessible packaging help users feel seen and catered to, boosting confidence and Net Promoter Scores (NPS).
Benefits for Brands:
Integrating AI and AR shortens product development cycles by up to 30%, replacing costly prototypes with digital sampling and virtual panels. Digital shade trials cut down on sample waste, and refill systems reduce plastic consumption.
Future Trends:
• AI-powered wearable skin health monitoring for hydration, UV exposure, and inflammation.
• Genomic personalization predicting sensitivities and aging patterns.
• Adaptive tools—voice-activated makeup stations, self-adjusting brushes, smart mirrors with haptic feedback.
• Cross-industry R&D collaborations to scale lab-to-market inclusive solutions.
Conclusion
Inclusive beauty tech is reshaping personal expression and industry standards. We’ve defined inclusive beauty tech, explored challenges, highlighted innovations—from AI shade matching and AR try-ons to adaptive packaging—and examined the impact on consumers and brands. As technology continues to evolve, it promises deeper personalization, eco-friendly practices, and universal access for all. Support inclusive beauty tech innovations by exploring brands that champion diversity in shade, packaging, and digital inclusivity.
FAQ
- What is inclusive beauty tech?
It’s the use of AI, AR, and adaptive design to make beauty products and experiences accessible and personalized for all skin tones, genders, ages, and abilities. - How do AR try-on apps work?
They use augmented reality to overlay virtual makeup on live video feeds, allowing users to experiment with products in real time before purchasing. - Why is packaging accessibility important?
Accessible packaging—like large-print labels, Braille markings, and ergonomic designs—ensures that users with disabilities can independently use beauty products. - What future trends should we watch?
Keep an eye on wearable skin sensors, genomic personalization of formulas, voice-activated makeup tools, and haptic-feedback smart mirrors.